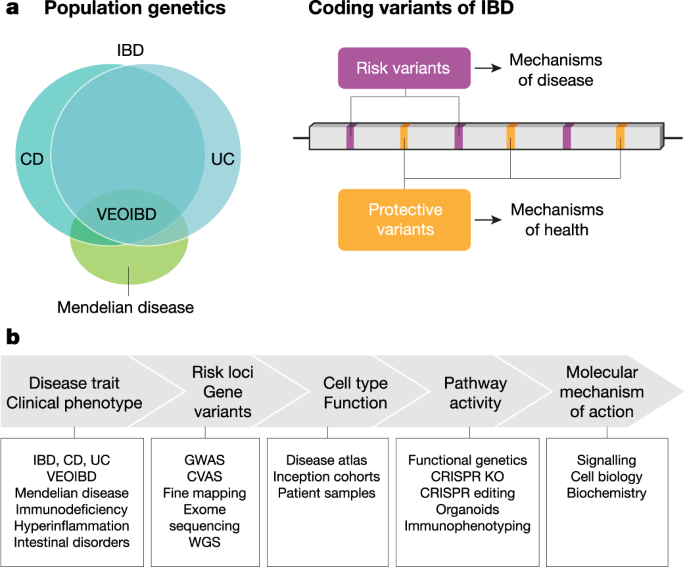
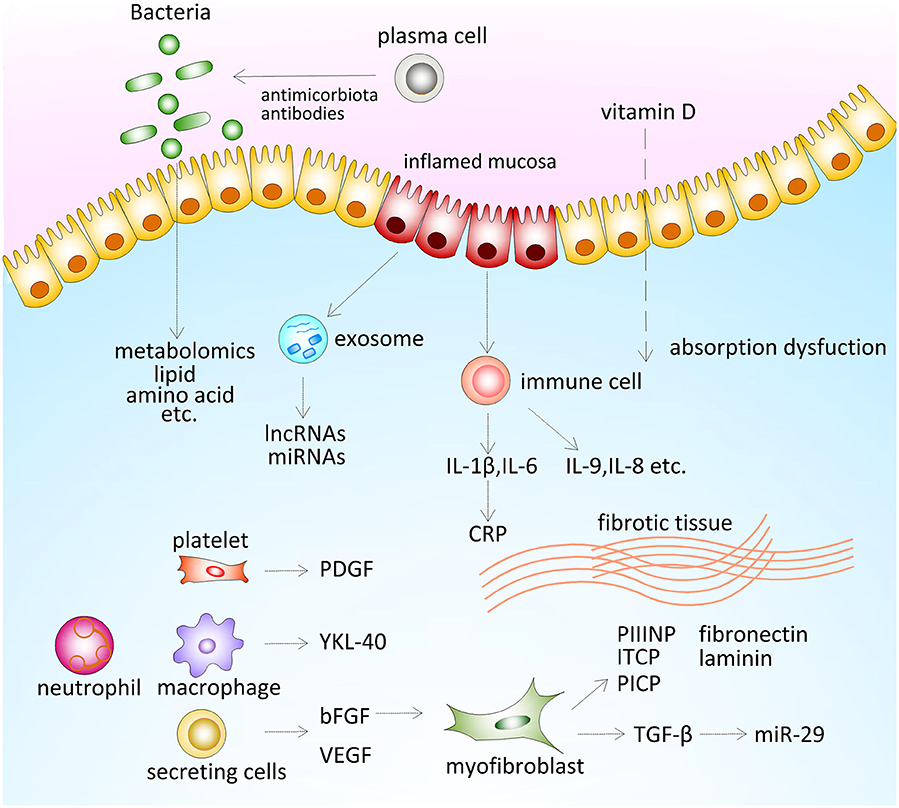
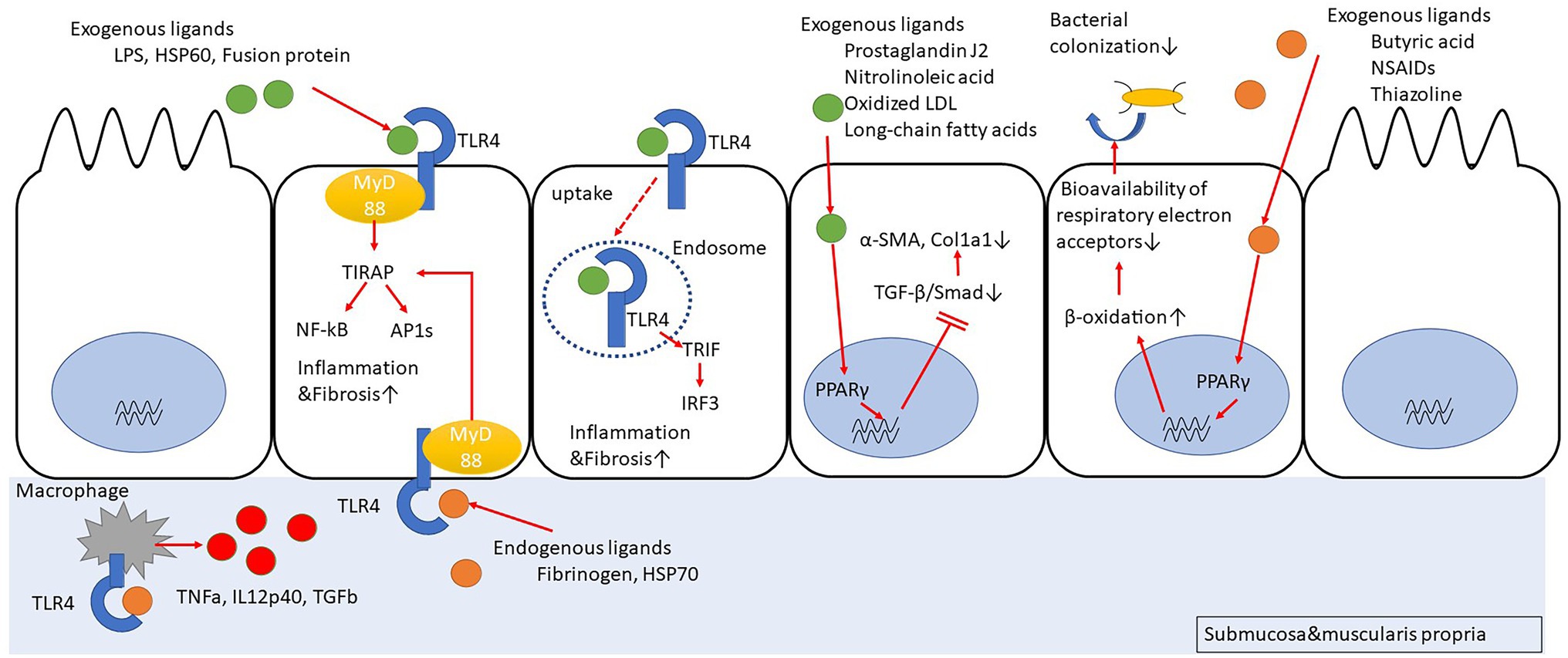
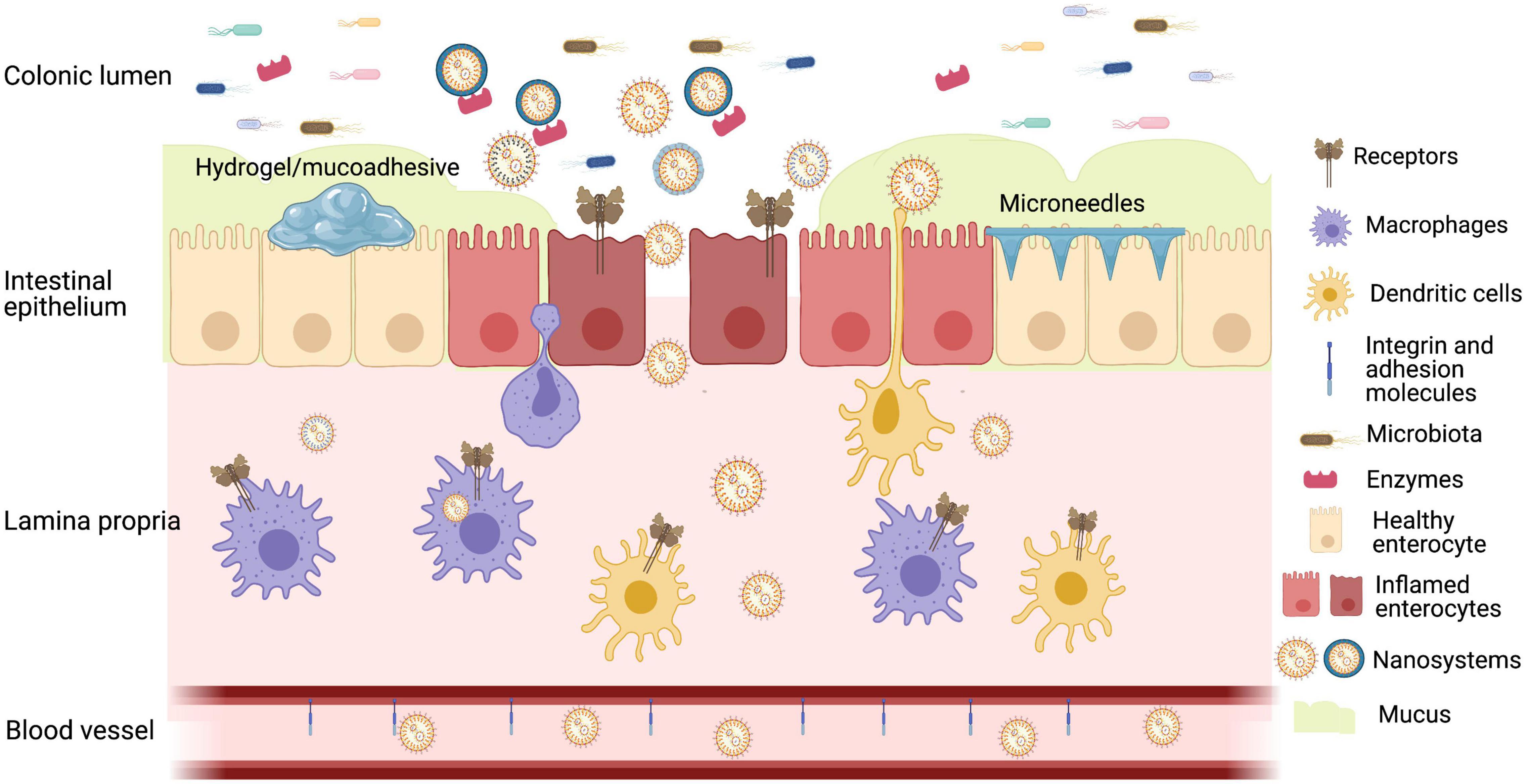
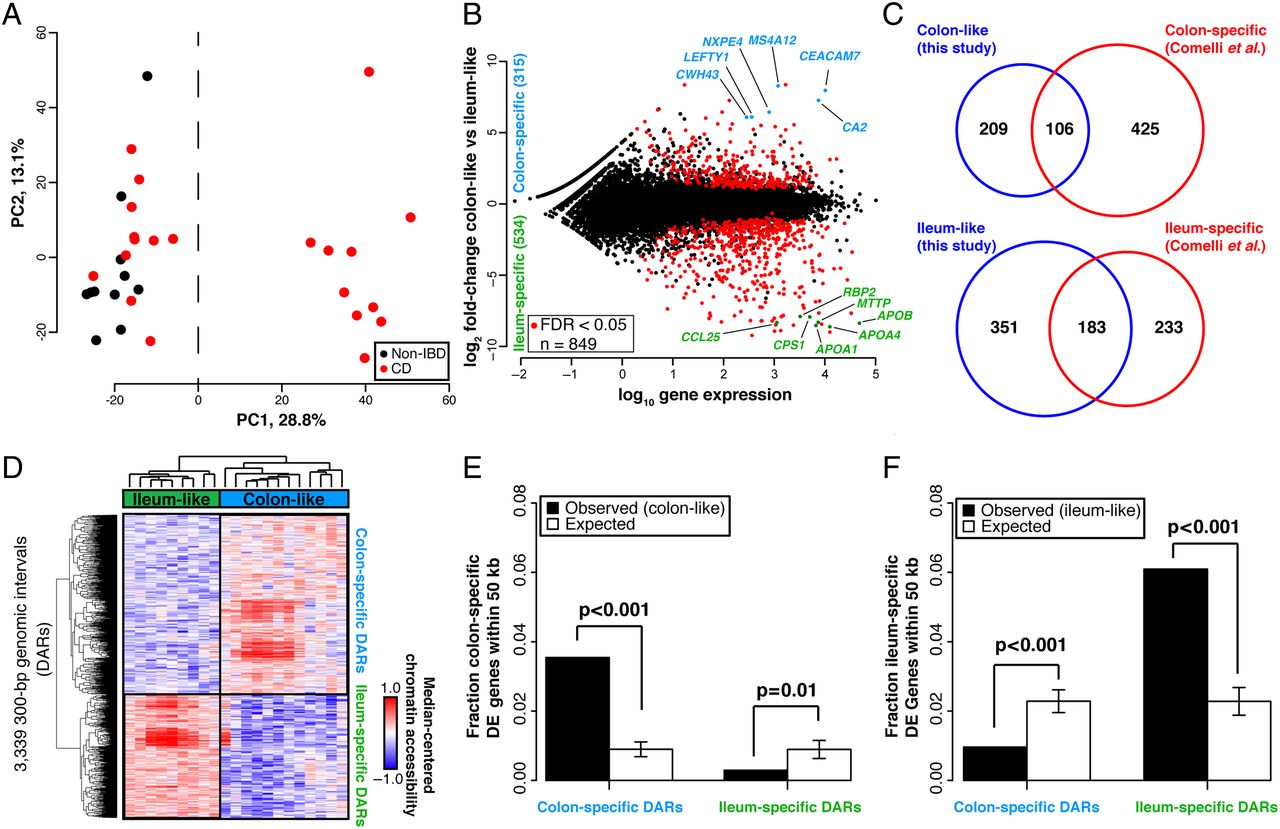
NCoR1 Protects Mice From Dextran Sodium Sulfate–Induced Colitis by Guarding Colonic Crypt Cells From Luminal Insult - ScienceDirect
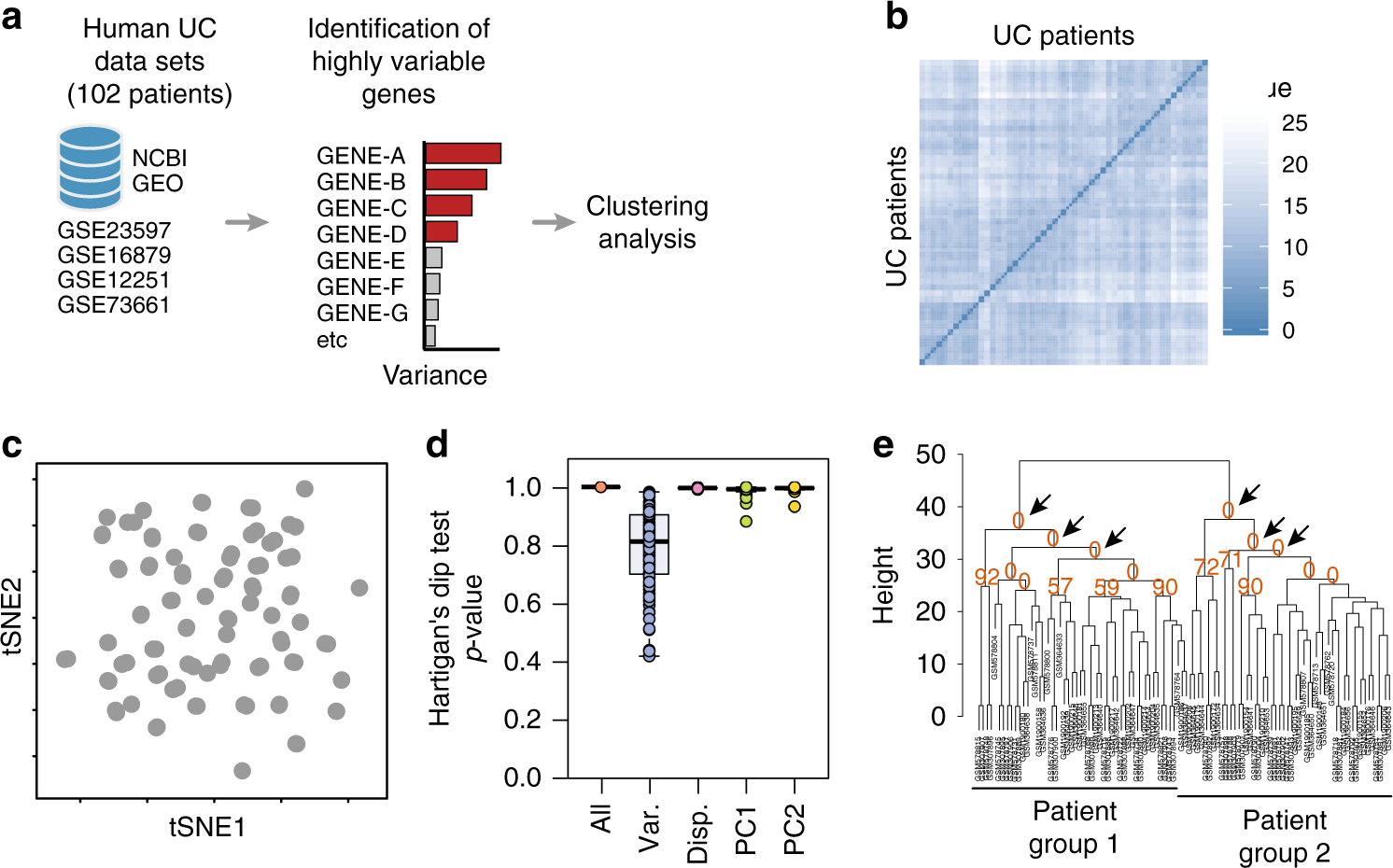
Conserved transcriptomic profile between mouse and human colitis allows unsupervised patient stratification | Nature Communications
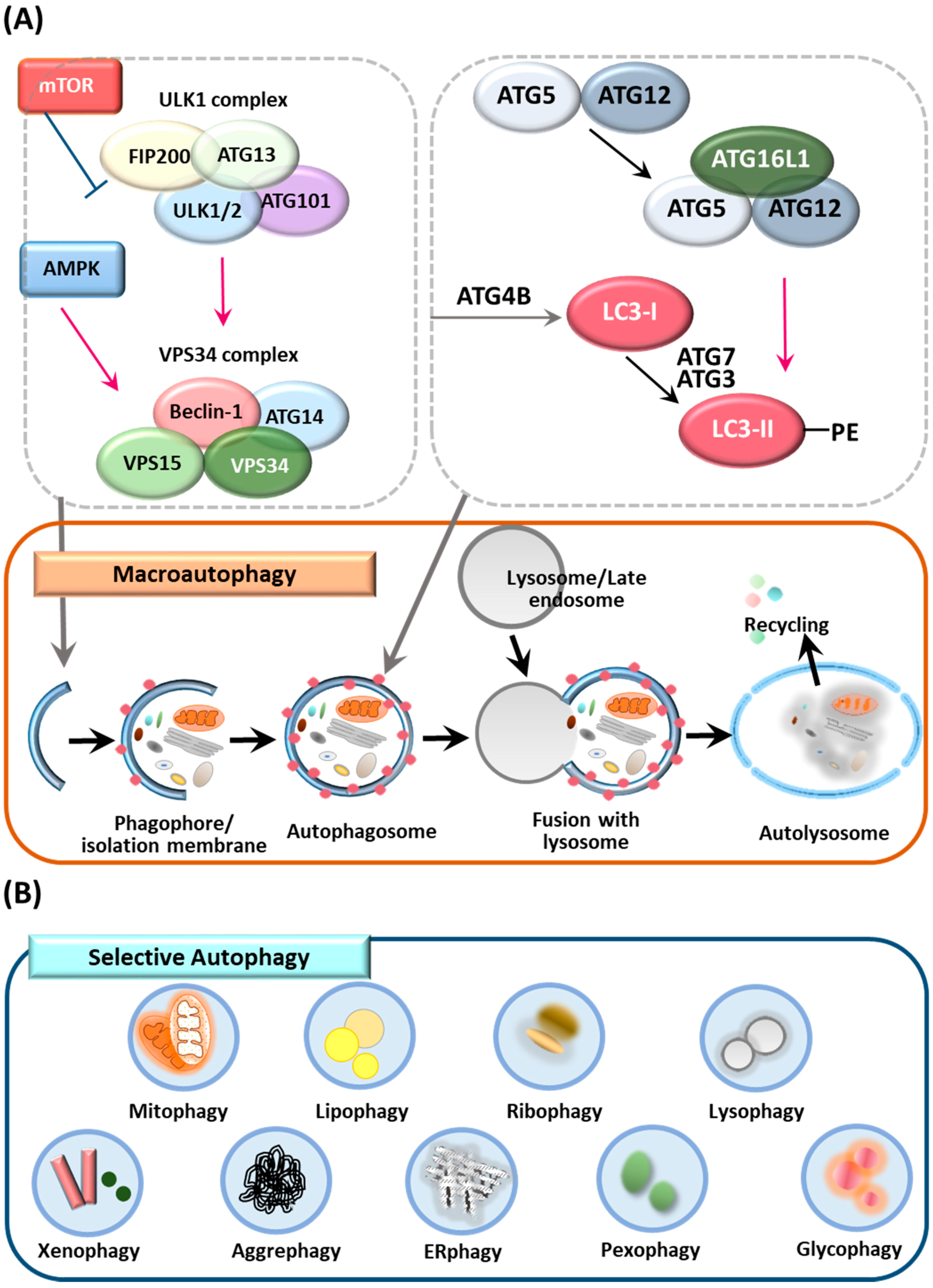
Cells | Free Full-Text | Roles of Autophagy-Related Genes in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease | HTML
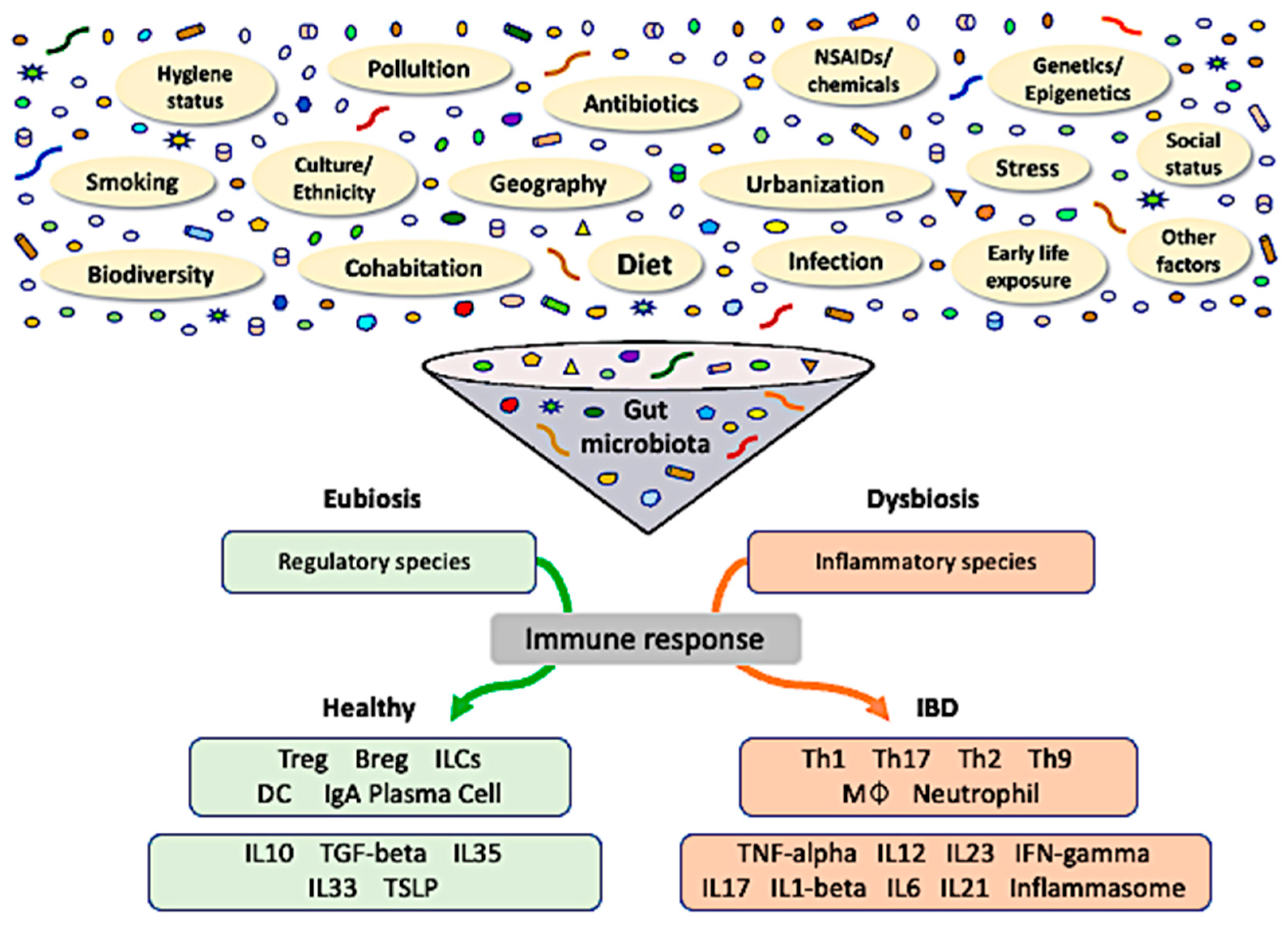
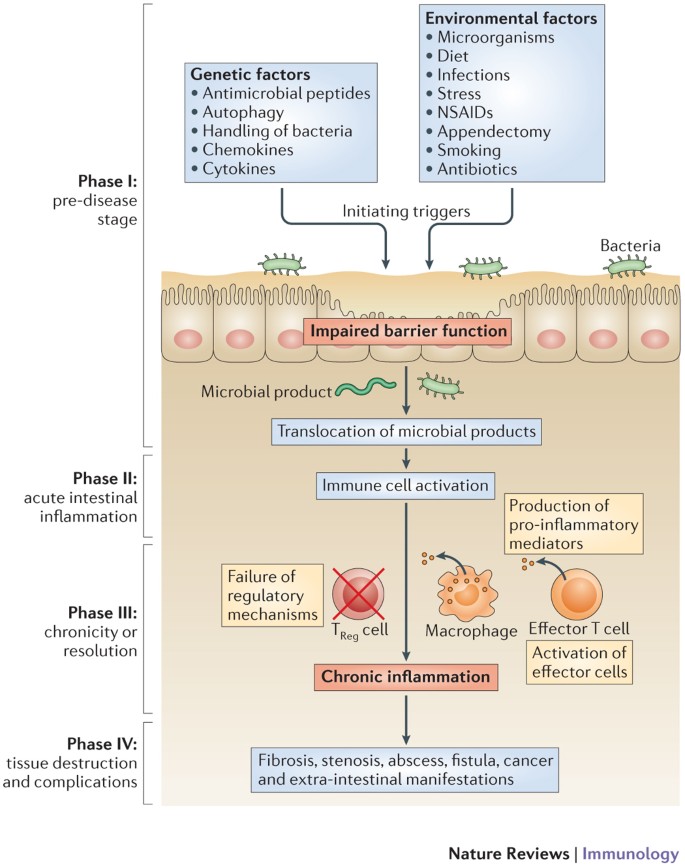
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenic Role and Potential Therapeutic Targets | HTML

Plant green pigment of chlorophyllin attenuates inflammatory bowel diseases by suppressing autophagy activation in mice | American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology

Comparative severity analysis of colitis in C57BL/6 than BALB/c mice: A novel and rapid model of DSS induced colitis | bioRxiv

Recent advances in inflammatory bowel disease: mucosal immune cells in intestinal inflammation | Gut
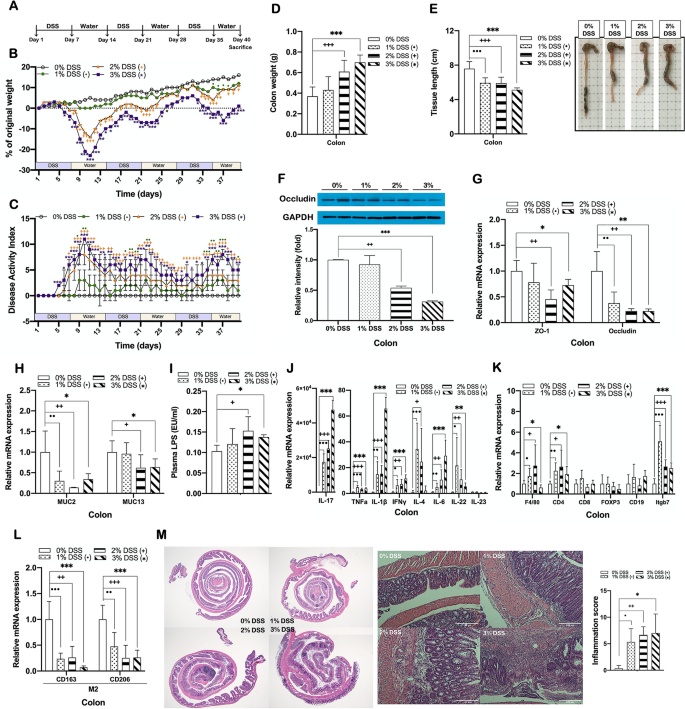
DSS-induced colitis is associated with adipose tissue dysfunction and disrupted hepatic lipid metabolism leading to hepatosteatosis and dyslipidemia in mice | Scientific Reports

Antibody signatures in inflammatory bowel disease: current developments and future applications: Trends in Molecular Medicine
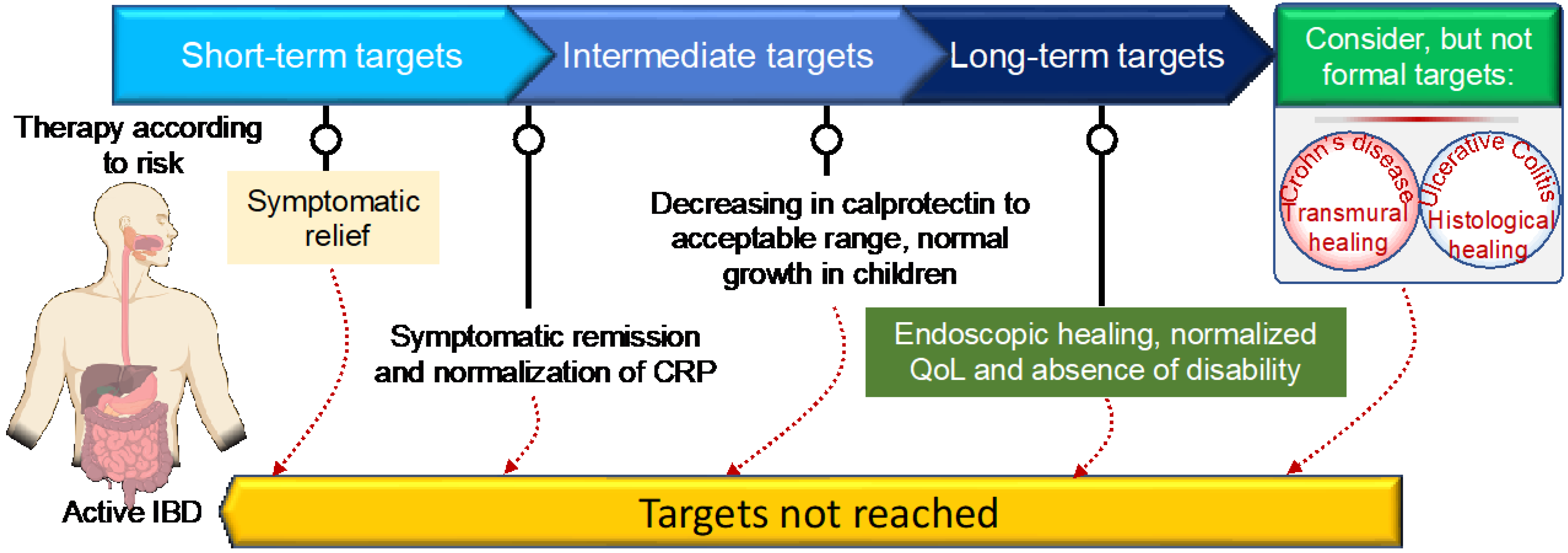
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatments and Predictive Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response | HTML

Reduction of inflammation and colon injury by a Pennyroyal phenolic extract in experimental inflammatory bowel disease in mice - ScienceDirect
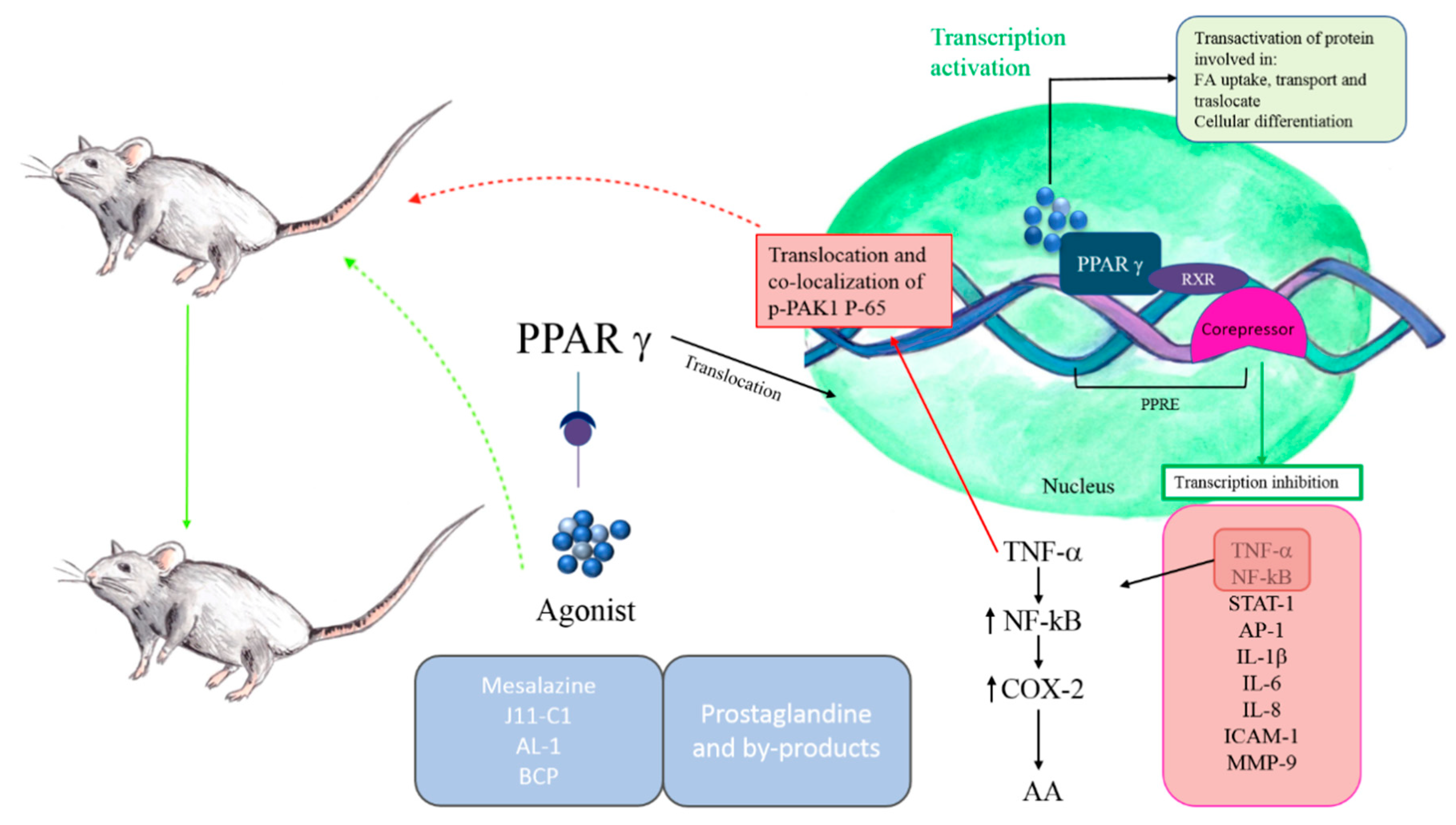
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Inflammatory Bowel Disease: New Insights into the Interplay between Environmental Factors and PPARγ | HTML

Targeting uPA-uPAR interaction to improve intestinal epithelial barrier integrity in inflammatory bowel disease - eBioMedicine

The role of the mitochondrial protein VDAC1 in inflammatory bowel disease: a potential therapeutic target: Molecular Therapy

Deletion of mucin 2 induces colitis with concomitant metabolic abnormalities in mice | American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology
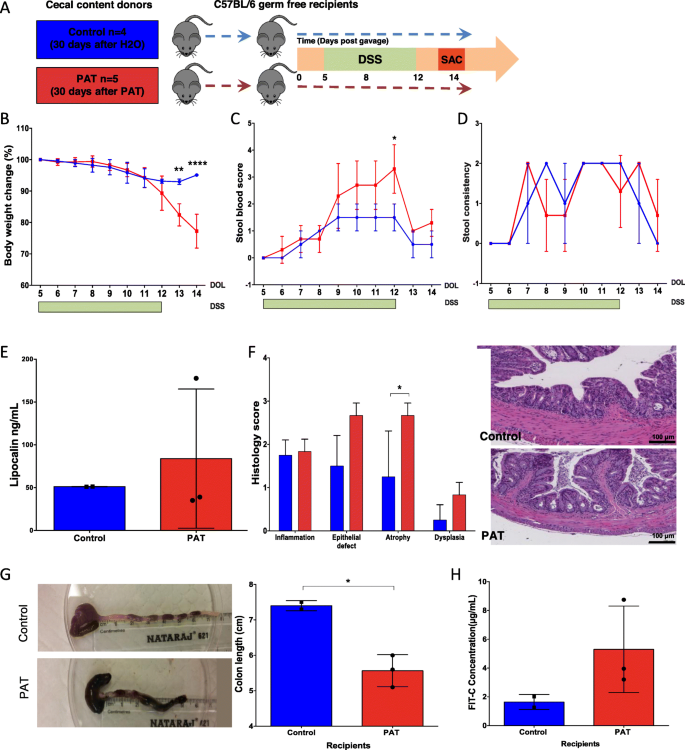
A single early-in-life antibiotic course increases susceptibility to DSS-induced colitis | Genome Medicine | Full Text

Biotin Supplementation Ameliorates Murine Colitis by Preventing NF-κB Activation - Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology

Koch's postulates, microbial dysbiosis and inflammatory bowel disease - Clinical Microbiology and Infection
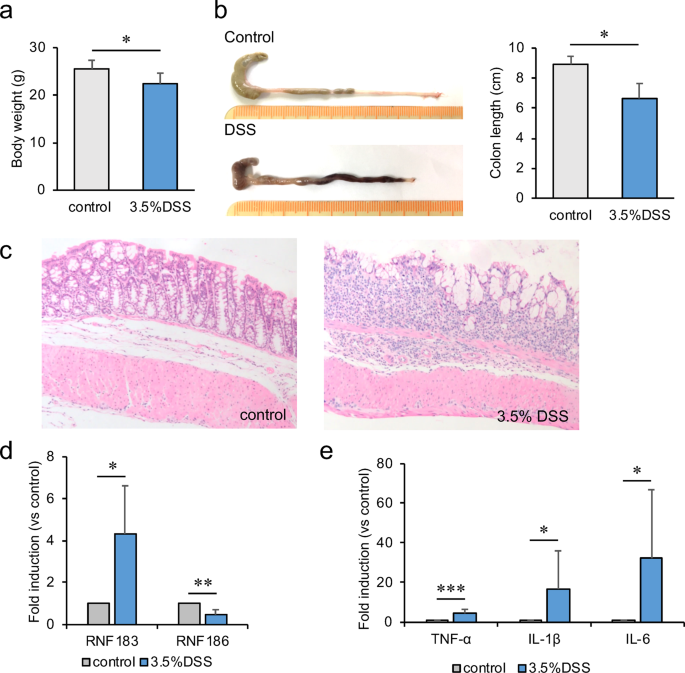
Inflammatory bowel disease-associated ubiquitin ligase RNF183 promotes lysosomal degradation of DR5 and TRAIL-induced caspase activation | Scientific Reports